
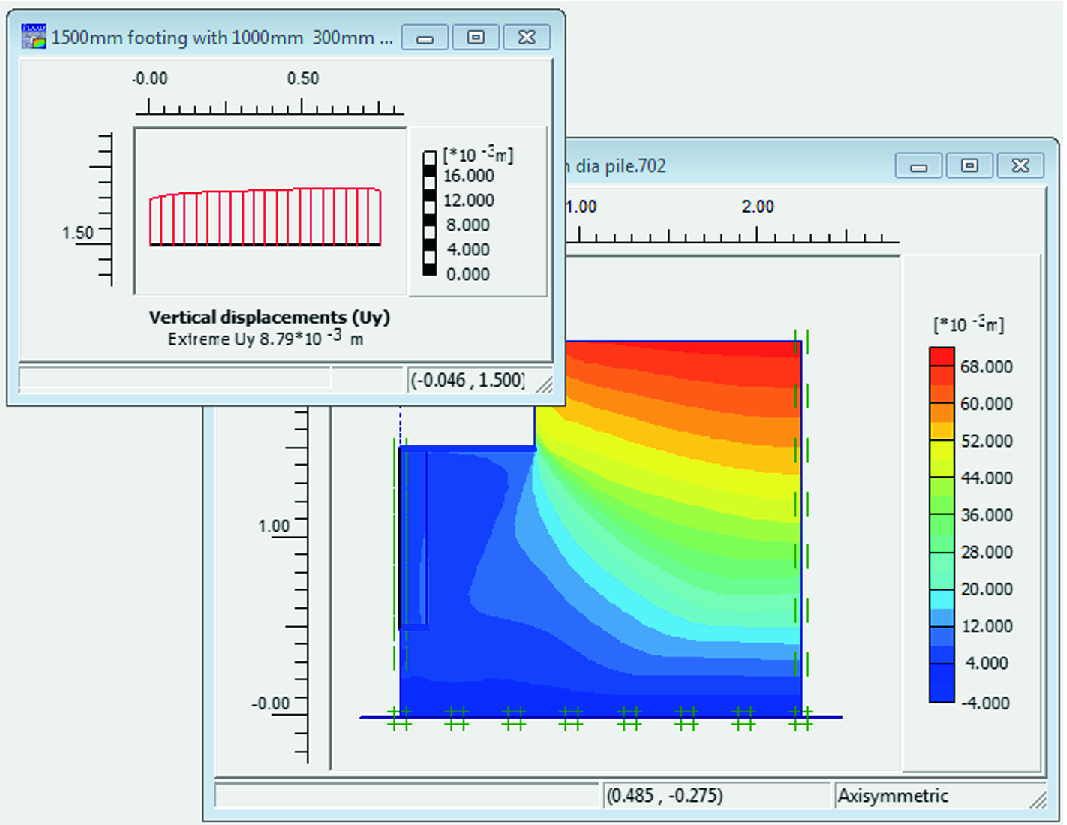

Vertical and lateral forces are applied to the head of the anchor in a. The material elements which can be represented in PLAXIS 2D dynamic are soil elements, beam elements, geogrid elements, node to node anchor, fixed end. Published in Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering ISSN 1674-7755 (Print) Publisher Elsevier Country of publisher China LCC subjects Technology: Engineering (General). PLAXIS 2DThe standard for 2D geotechnical analysis This paper presents the. To demonstrate the solution of an axisymmetric pressure vessel using the stiffness method. To derive the axisymmetric element stiffness matrix, body force, and surface traction equations. A good agreement in their comparative study for pullout response is also observed. Chapter 9 Axisymmetric Elements Learning Objectives To review the basic concepts and theory of elasticity equations for axisymmetric behavior. Common Mistakes on the Application of Plaxis 2D in Analyzing Excavation Problems GOUW Tjie-Liong Civil Engineering Department, Bina Nusantara University, 11480 Jakarta, Indonesia Email : gouw3183binus.ac.id Abstract The advance of computer technology has made the finite element method (FEM) more accessible than ever. In the absence of literature regarding numerical modelling of helical soil nail, simulation results are validated with uplift responses of helical piles and soil anchors. The response of helical soil nail using axisymmetric finite element simulation is found similar to the uplift behaviour of helical piles and helical soil anchors. The helical plate spacing ratio (s/Dh) and diameter ratio (Dh/Ds) are found to increase the pullout only up to a critical value. The pullout capacity is found to increase with increase in number of helical plates. The failure surfaces for various helical soil nail configurations and their pullout mechanisms are also analysed and discussed. The effect of varying number of helical plates, helical plate spacing and helical plate diameter is studied to understand the pullout capacity behaviour. The numerical modelling of actual pullout response is achieved by axisymmetric and horizontal loading condition. An investigation into the pullout response of helical soil nail using finite element subroutine Plaxis 2D is presented.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
